SN-GAN簡介 - Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks
Takeru Miyato, Toshiki Kataoka, Masanori Koyama, Yuichi Yoshida. “Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks”. ICLR 2018
ICLR 2018 paper (oral)
Openreview : https://openreview.net/forum?id=B1QRgziT-
Paper Link : https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05957
Github code(Chainer) : https://github.com/pfnet-research/sngan_projection
此團隊於 ICLR 2018 發佈了兩篇論文:
- Takeru Miyato, Toshiki Kataoka, Masanori Koyama, Yuichi Yoshida. Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks. ICLR2018.
- Takeru Miyato, Masanori Koyama. cGANs with Projection Discriminator. ICLR2018.
此論文的前作為:
Yuichi Yoshida and Takeru Miyato. Spectral norm regularization for improving the generalizability of deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.10941, 2017.
若對理論有不懂的可以翻這篇論文。
下圖為 SN-GAN 以及 cGANs with Projection Discriminator 兩論文結合的結果。

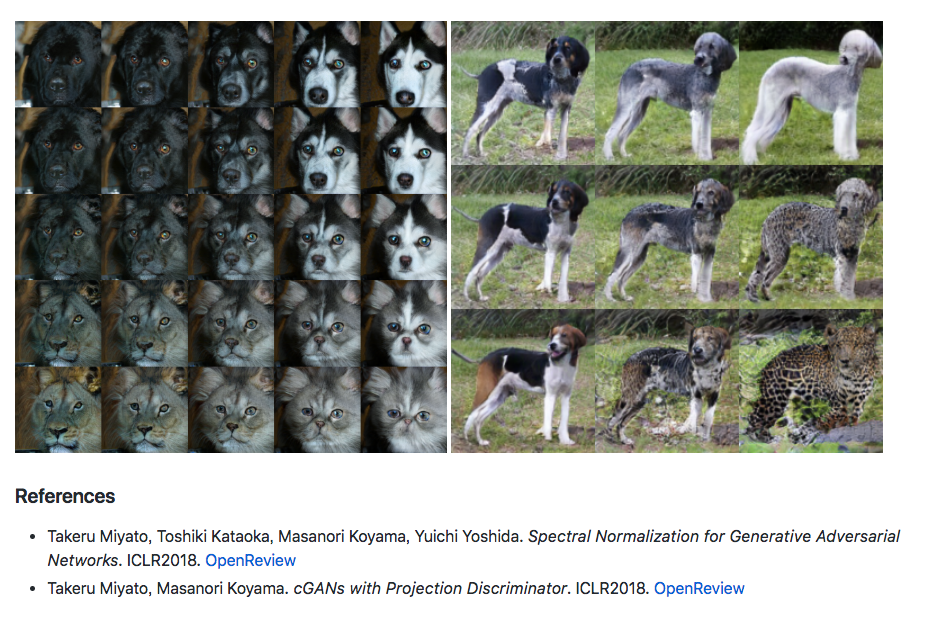
備註:
這篇很難,論文很多數學式,下方的數學決定簡單帶過,此篇做了很多實驗並與各個方法的比較及分析,共計26頁,有興趣的去看論文。
簡介
GAN 最常見的問題就是訓練時會不穩定,
而此論文提出了一個新的 weight normalization 的方式 - spectral normalization,
Spectral normalization 主要想法是透過 Lipschitz constant 對每層的輸出做限縮,
簡單實作且僅需少數的計算量。
並提出圖像合成模型 Spectrally Normalized GANs(SN-GAN),
使用此架構在 CIFAR10, STL-10, and ILSVRC2012 等資料集訓練,
成果不錯並且減少了 Mode collapse 的問題,
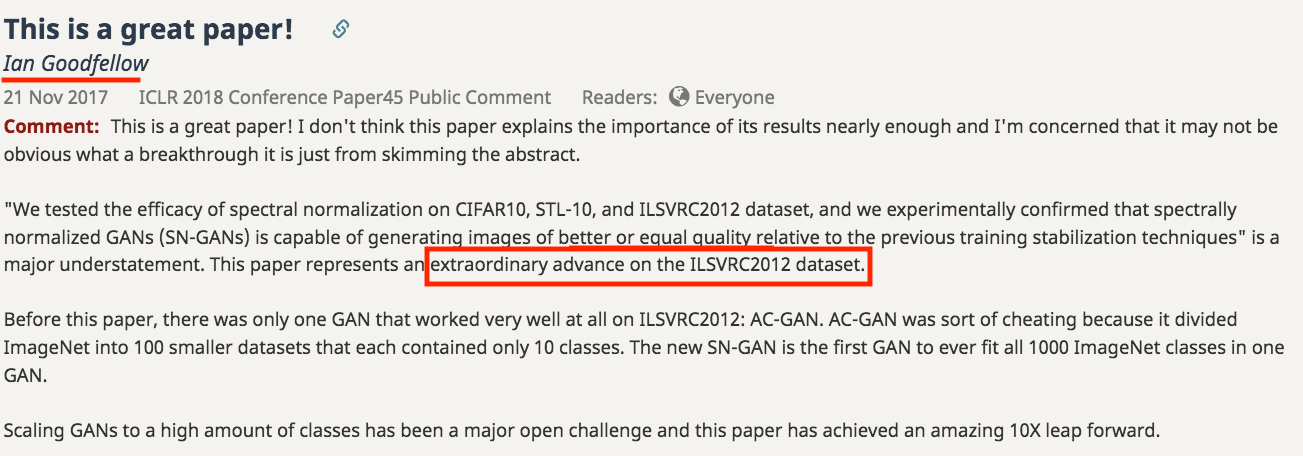
並且 Goodfellow 在 OpenReview 中稱讚此篇論文。((會在下方陸續提到稱讚的地方,
作者有提供 Code, 基於深度學習框架 - Chainer。
Spectrally Normalized
特性為:
- 主要想法為控制 Lipschitz constant,不需複雜的參數調整。
- 實作簡單並且計算需求少。

此處的 norm 為 l2-norm,
下方可看作對該點做斜率/輸出的限縮,希望在 x 位移時 y 不要移動的太多。
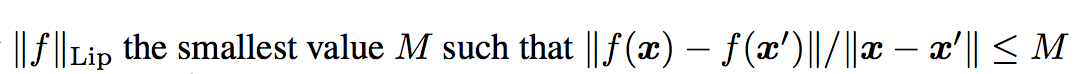
對 Lipschitz norm 做解釋,
若對這部分的參數或是證明不清楚的,
提供幾個連結參考:
- Wiki:Matrix norm
- 知乎:非凸优化基石:Lipschitz Condition
- encyclopediaofmath:Lipschitz constant
- stackexchange:Why does the spectral norm equal the largest singular value?
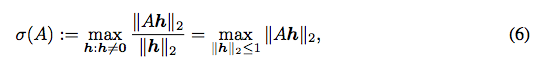
σ 其實就是在得出最大奇異值(Singular value),
可用 singular value decomposition (SVD) 求得。
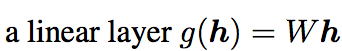
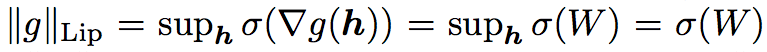
而當|a|Lip = 1時,有著此特性:
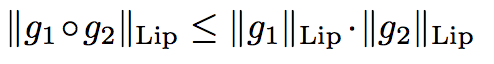
因此對每層都做 Lip-1 限縮即為對整個 Model 做 Lip-1。
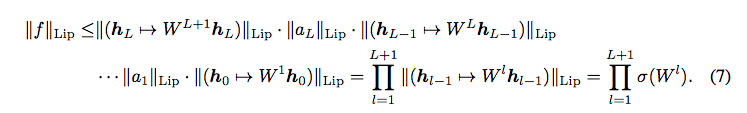

而整個 Spectral normalization 就是 eq8 的想法,
| 對每層的輸出做限縮,這樣可讓輸出 | f | Lip 不會超過 1。 |
如果不知道為什麼,想看相關推倒的話建議看這個,寫得很好:Spectral Normalization Explained
加快得出 Spectral normalization - Fast approximation Spectrally Normalized
如果對每層 W 都使用 σ (SVD方法) 得出最大的奇異值這樣計算資源太昂貴,
SVD 方法:

而此處提出使用 power iteration 來求得最大的奇異值,
構想如下,eq18. 透過兩個參數除以自己的上界來趨近於 eq.19, 達成 SN 的效果。
這部分我看論文沒詳細述說,有需要補充的歡迎留言。
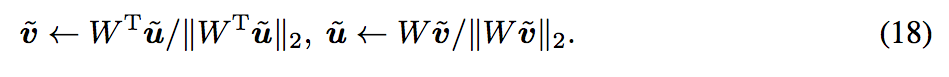

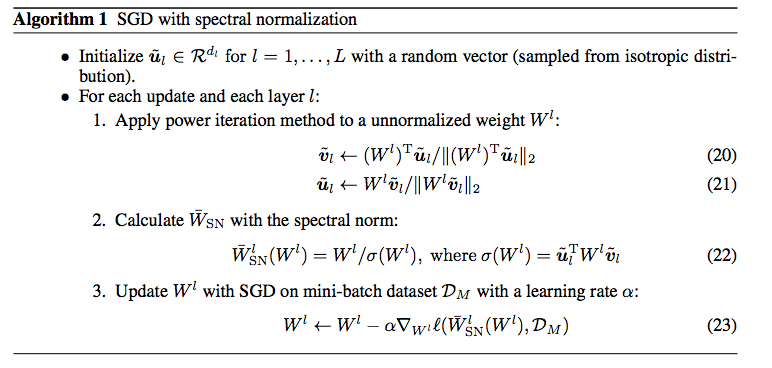
下方給出兩個版本的演算法,
一個為本文 SN-GAN,
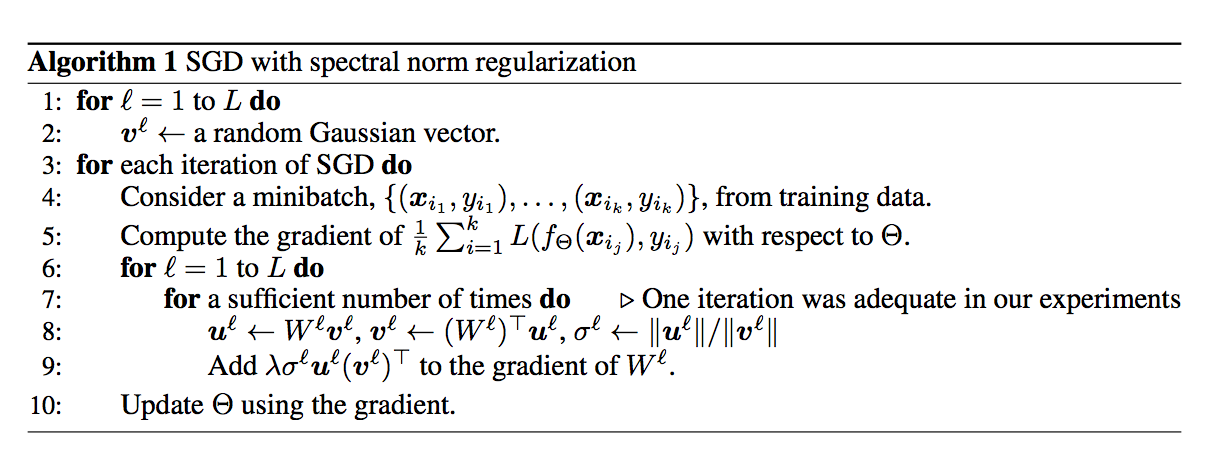
另一個為此團隊前作 Spectral Norm Regularization for Improving the Generalizability of Deep Learning ,
前作概念與本文相近不過他是將SN當作Regression,
我認為看後者的可能會比較能理解,然後再看本文的。
本文 SN-GAN 給出的演算法
而這邊 power iteration 的 iteration 次數僅需 1 次,
因為每層 layer 的 w 經過每次訓練其實只是做微調,調整完的 wi+1 會相近於 wi,
所以我們可以一直沿用 u 去做下一次的迭代。
Spectral Norm Regularization for Improving the Generalizability of Deep Learning 給的演算法
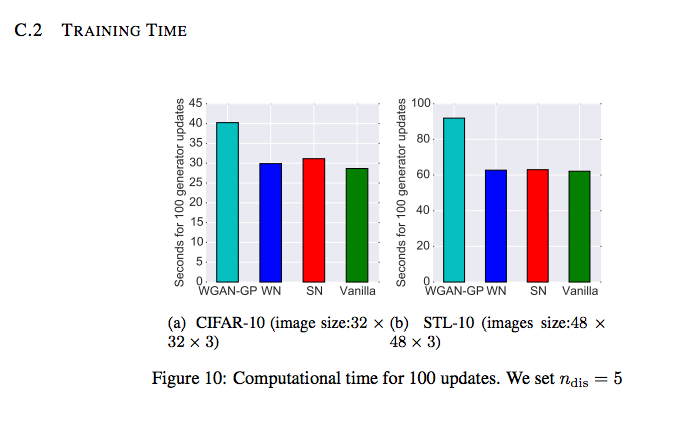
透過 Fast approximation 計算速度比較
Hinge Loss
先前已有論文揭露 Hinge loss
Jae Hyun Lim and Jong Chul Ye. Geometric GAN. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.02894, 2017.
Dustin Tran, Rajesh Ranganath, and David M Blei. Deep and hierarchical implicit models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.08896, 2017
原本的 GAN Loss Function 如下:
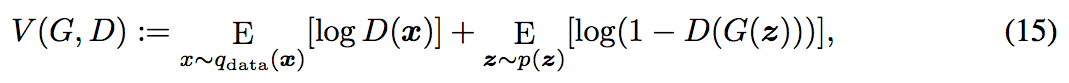
Hinge Loss 如下
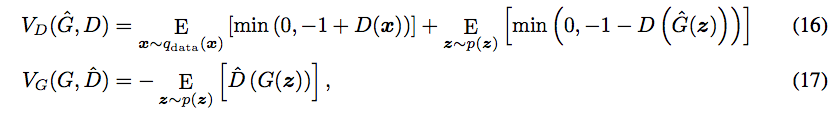
eq - 16
d_loss_real = torch.nn.ReLU()(1.0 - d_out_real).mean()
d_loss_fake = torch.nn.ReLU()(1.0 + d_out_fake).mean()
d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake
eq - 17
g_loss_fake = - g_out_fake.mean()
實際 hinge loss 用法可看此篇(Pytorch) Github:Self-Attention-GAN
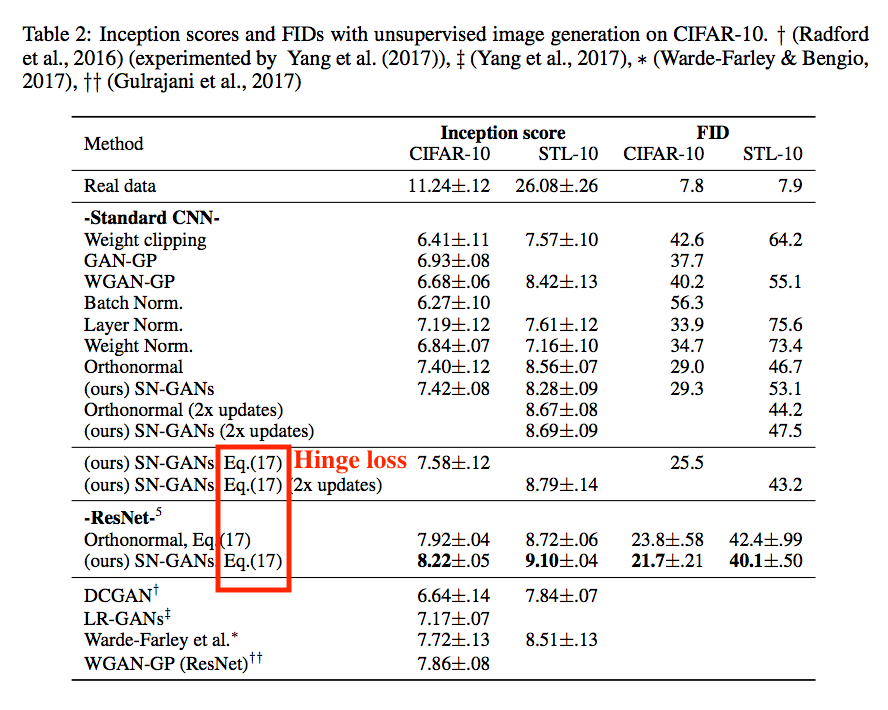
與其他方法相比(請去看論文)
對下面幾個方法做比較
- WEIGHT NORMALIZATION AND FROBENIUS NORMALIZATION
- WEIGHT CLIPPING
- SINGULAR VALUE CLIPPING AND SINGULAR VALUE CONSTRAINT
- WGAN WITH GRADIENT PENALTY (WGAN-GP)
- Orthonormal regularization
從下表可看出 SN 在多參數都有較好的穩定度,
 IS 評比
IS 評比 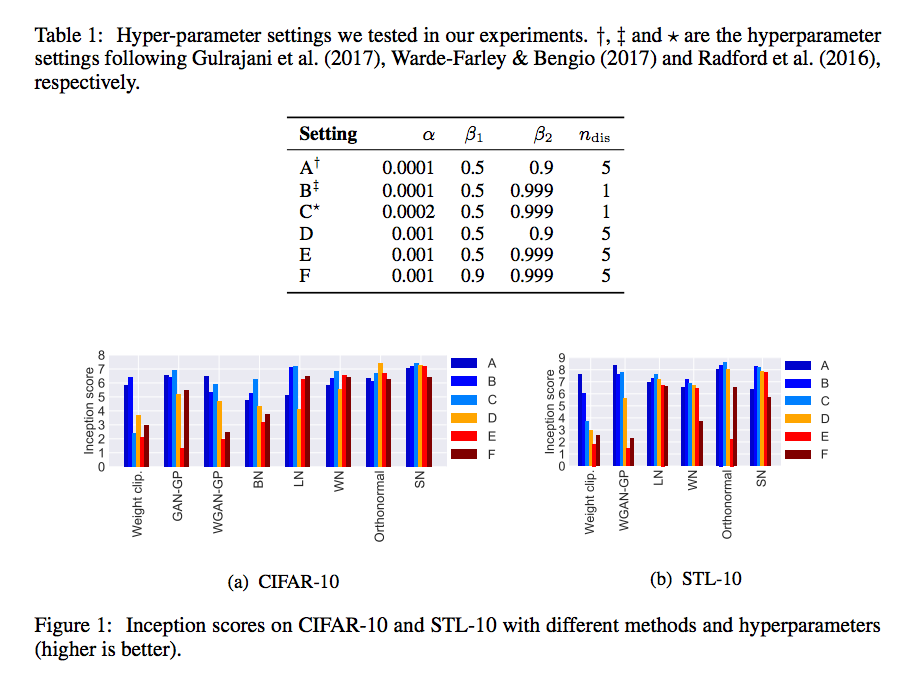
FID 評比 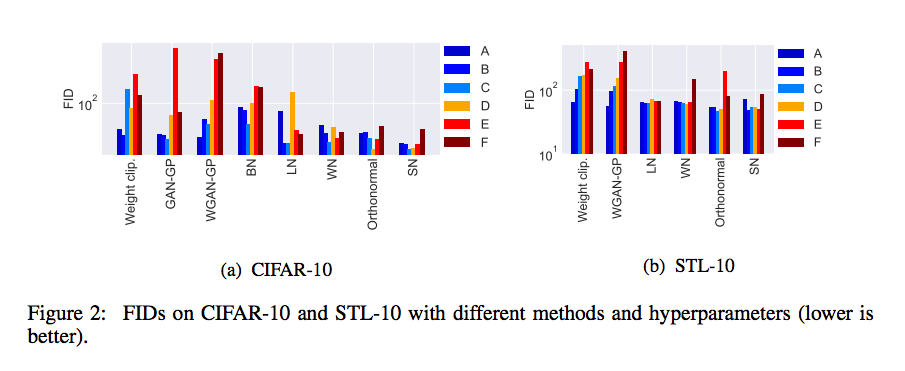
實作相關
在pytorch 0.4.1 版中已有 SpectralNorm
源碼可見此 spectral_norm - pytorch
比較關鍵的部分如下
def compute_weight(self, module):
weight = getattr(module, self.name + '_orig')
u = getattr(module, self.name + '_u')
weight_mat = weight
if self.dim != 0:
# permute dim to front
weight_mat = weight_mat.permute(self.dim,
*[d for d in range(weight_mat.dim()) if d != self.dim])
height = weight_mat.size(0)
weight_mat = weight_mat.reshape(height, -1)
with torch.no_grad():
for _ in range(self.n_power_iterations):
# Spectral norm of weight equals to `u^T W v`, where `u` and `v`
# are the first left and right singular vectors.
# This power iteration produces approximations of `u` and `v`.
v = normalize(torch.matmul(weight_mat.t(), u), dim=0, eps=self.eps)
u = normalize(torch.matmul(weight_mat, v), dim=0, eps=self.eps)
sigma = torch.dot(u, torch.matmul(weight_mat, v))
weight = weight / sigma
return weight, us
實驗設定及結果:
參數設定: α = 0.0002, β1 = 0, β2 = 0.9, ndis = 5
網路架構: 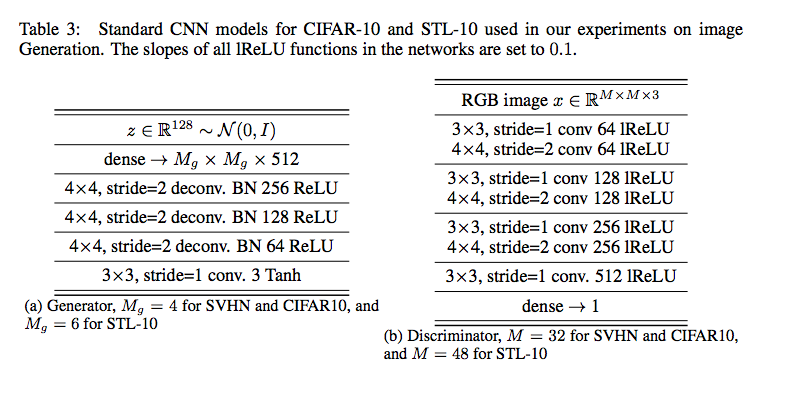
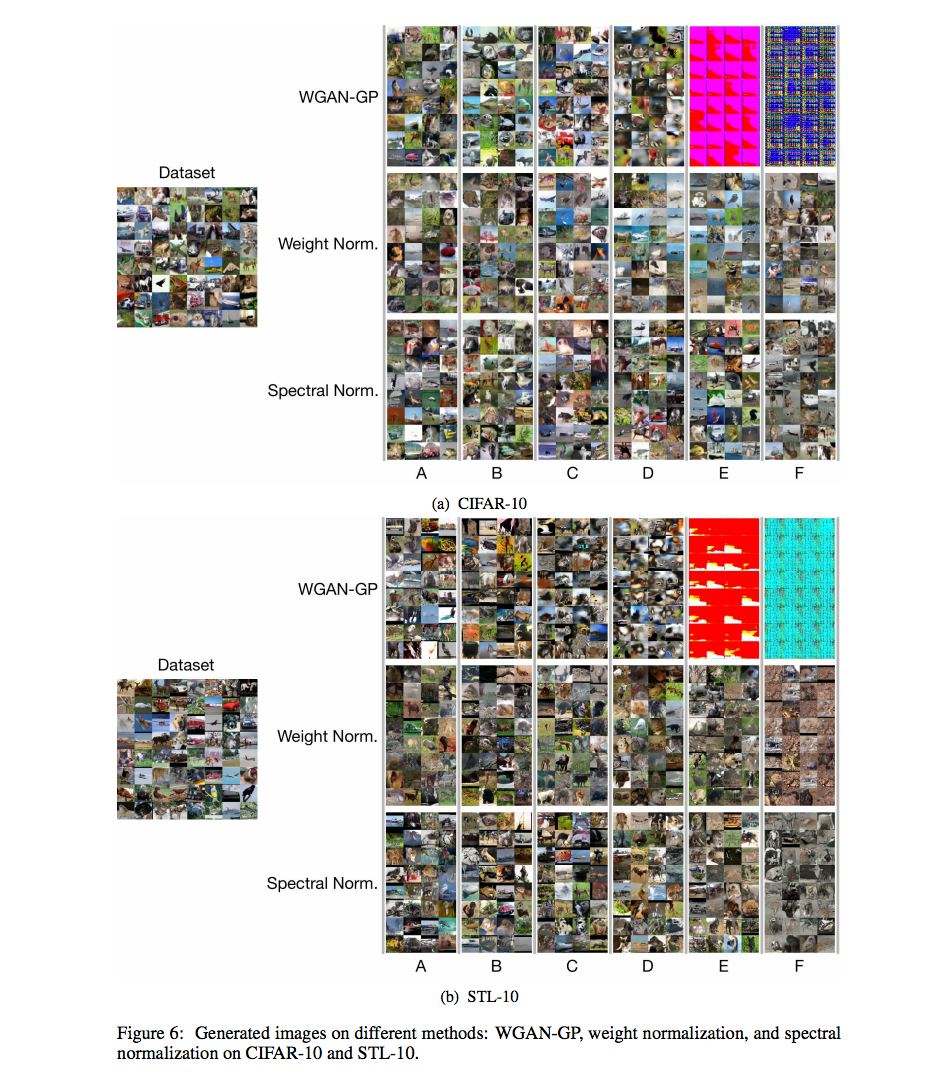
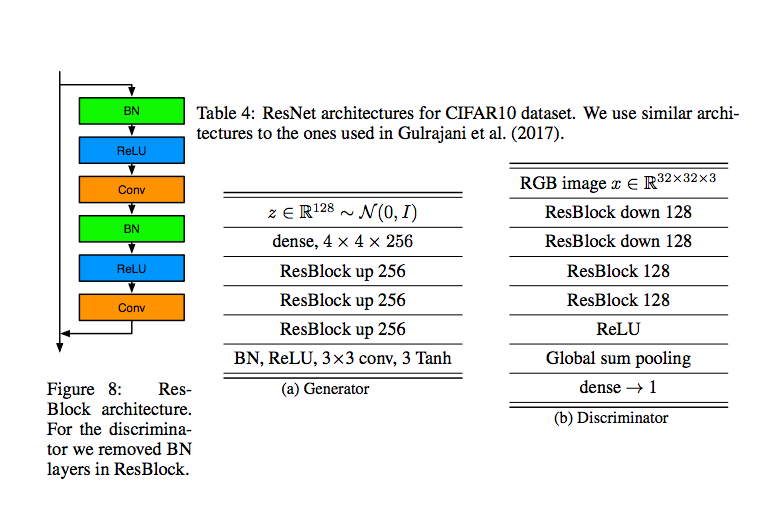


上圖為此篇被 GoodIanFellow 大讚的部分,
它能夠訓練 ILSVRC2012 並且沒有嚴重的 Mode collapse 問題,
這之前只有 AC-GAN 能做到, 但是 AC-GAN 有點作弊,
AC-GAN1個模型訓練10個類別,共訓練了100個模型才能夠達到生成 ILSVRC2012 的 1000個類別。
但這篇只需要一個模型即可生成出 1000 個類別。
延伸閱讀:
此方法被廣泛應用於 2018 年的 GAN 相關論文中,下方論文為基於此方法的延伸:
SA-GAN - (Goodfellow 等人提出的圖像合成任務)
Han Zhang, Ian Goodfellow, Dimitris Metaxas, Augustus Odena. “Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks”.arXiv:1805.08318
BigGAN - (基於 SA-GAN 以及 SN-GAN 概念)投遞至 ICLR 2019,過幾天我再把此篇簡介補上。
Andrew Brock, Jeff Donahue, Karen Simonyan. “Large Scale GAN Training for High Fidelity Natural Image Synthesis”.arXiv:1809.11096 OpenReview:Large Scale GAN Training for High Fidelity Natural Image Synthesis
參考資料:
OpenReview:Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks
Spectral Norm Regularization for Improving the Generalizability of Deep Learning
Spectral Normalization Explained
PR 087 Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks